Liquid Nitrogen Tanks in Laboratory Applications: Safeguarding Embryo Samples
In the realm of scientific research and medical advancements, the preservation of biological samples is paramount. Among the various methods employed for this purpose, the use of liquid nitrogen tanks has emerged as a critical component, particularly in laboratories dealing with sensitive materials such as embryo samples. This article explores the application of liquid nitrogen tanks in laboratories, focusing on their significance in the preservation and storage of embryo samples.
Liquid nitrogen, a cryogenic liquid with a boiling point of -196 degrees Celsius, is widely utilized in laboratories for its ability to maintain extremely low temperatures. This characteristic is essential for the long-term preservation of biological specimens, including embryos, which are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. The use of liquid nitrogen tanks allows researchers and medical professionals to store these samples in a stable environment, significantly extending their viability for future use.
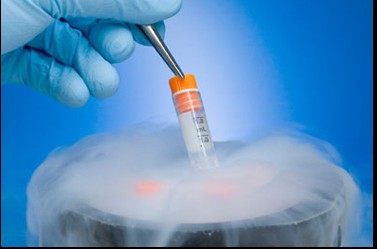
One of the primary applications of liquid nitrogen tanks in laboratories is the cryopreservation of embryos. Cryopreservation is a process that involves cooling and storing embryos at ultra-low temperatures to halt all biological activity, effectively putting them in a state of suspended animation. This technique is particularly valuable in reproductive medicine, where embryos may be created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) and need to be preserved for future implantation. By utilizing liquid nitrogen tanks, laboratories can ensure that these embryos remain viable for extended periods, allowing for flexibility in treatment plans and increasing the chances of successful pregnancies.
Moreover, the use of liquid nitrogen tanks is not limited to the storage of embryos. They are also employed in various other laboratory applications, including the preservation of stem cells, sperm, and oocytes. The ability to maintain these biological materials at cryogenic temperatures is crucial for research and clinical applications, as it allows scientists to study cellular behavior, genetic material, and potential therapeutic uses without the risk of degradation.
In addition to their role in preservation, liquid nitrogen tanks also facilitate the transportation of biological samples. When samples need to be moved between laboratories or to different facilities, maintaining the integrity of the specimens is essential. Liquid nitrogen tanks provide a reliable means of transport, ensuring that samples remain at the required low temperatures throughout the journey. This capability is particularly important in the context of collaborative research efforts, where samples may need to be shared across institutions.
Safety is a critical consideration when working with liquid nitrogen tanks. Laboratories must adhere to strict safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of personnel. Proper training in handling cryogenic materials, along with the use of appropriate protective equipment, is essential to mitigate risks associated with liquid nitrogen exposure. Additionally, laboratories must implement regular maintenance and monitoring of liquid nitrogen tanks to ensure their functionality and prevent potential failures that could compromise sample integrity.
In conclusion, liquid nitrogen tanks play a vital role in laboratory applications, particularly in the preservation of embryo samples. Their ability to maintain ultra-low temperatures allows for the long-term storage of sensitive biological materials, facilitating advancements in reproductive medicine and research. As laboratories continue to explore the potential of cryopreservation and other applications, the importance of liquid nitrogen tanks will only grow, underscoring their significance in the scientific community. By ensuring the safe and effective storage of embryo samples, these tanks contribute to the ongoing pursuit of knowledge and innovation in the field of biology and medicine.
















 Products
Products